Contact person
Rohan Koder
Technical Consultant

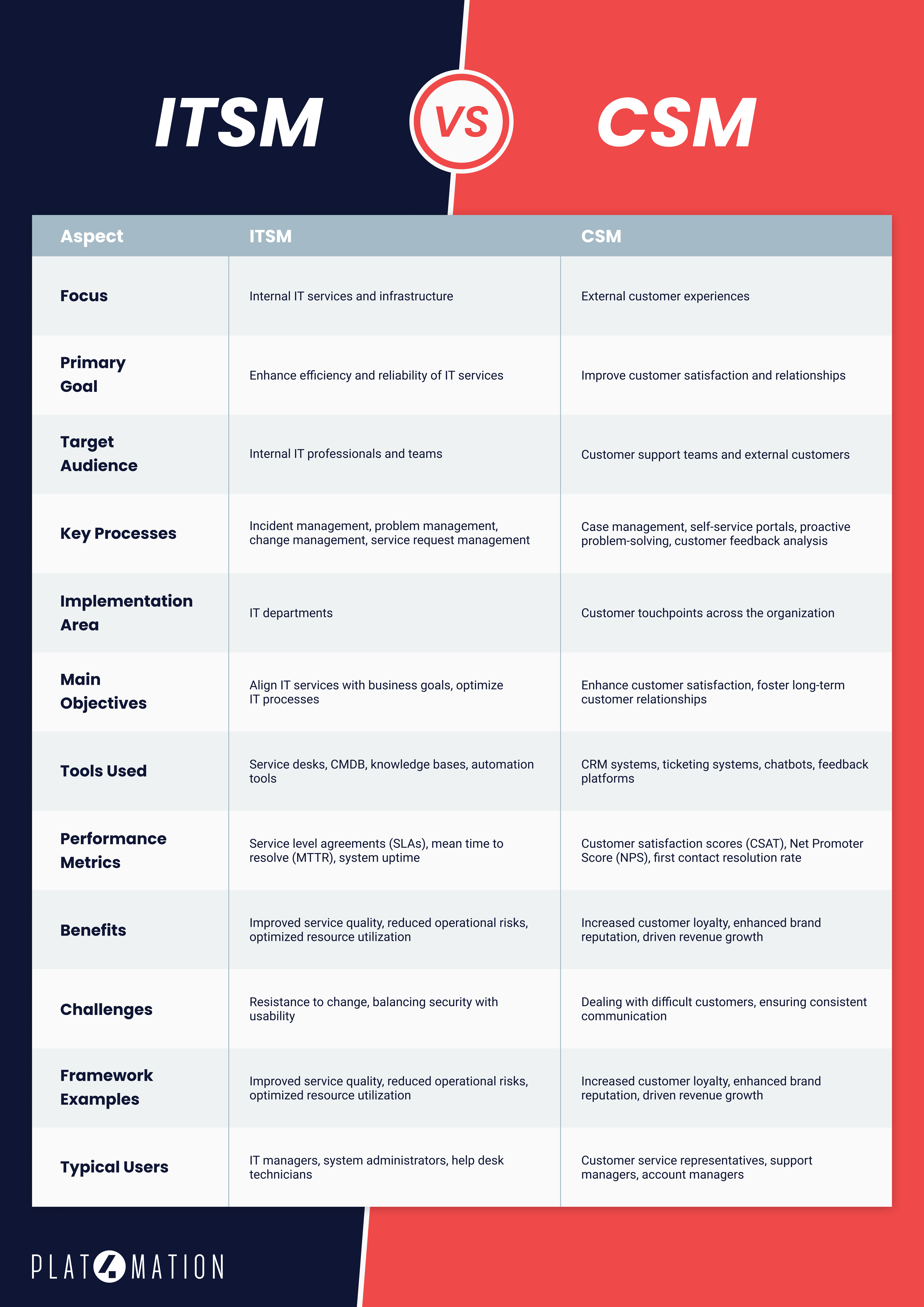
ServiceNow ITSM (IT Service Management) vs CSM (Customer Service Management) is an important distinction for organizations focused on providing quality services to both internal and external customers.
I’m Rohan Koder, and I’ll guide you through the key differences between ServiceNow ITSM vs CSM, showing how these solutions streamline IT operations and elevate customer satisfaction!
IT Service Management (ITSM) is centered around managing IT services and ensuring that IT teams can deliver high-quality services to internal users (employees) or external clients. It focuses on optimizing IT service delivery through a set of practices
Customer Service Management (CSM) focuses on improving customer experiences by managing customer interactions, complaints, and inquiries efficiently. It’s a broader approach that includes helping external customers resolve issues, offering customer support, and enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
1. Case Management
2. Omni-channel Support
3. Customer Portal
4. Knowledge Management
5. Field Service Management
ITSM primarily supports internal employees or other departments within the organization. It ensures that the organization’s IT infrastructure runs smoothly to avoid downtime, service interruptions, and technology bottlenecks.
The primary focus is on supporting internal employees by providing everything they need to perform their roles effectively. For example, an internal shop in the factory that provides all the hardware and software assistance to their employees. The goal is to ensure smooth operations without any disruptions.
Scope and Integration
ITSM integrates with other IT systems like monitoring tools, IT asset management systems, and CMDBs (Configuration Management Databases) to offer complete visibility into IT infrastructure.
The main goal of CSM is to keep the customer happy and solve their problem through various channels like phone, email, chat, etc.
CSM focuses on supporting the customers, just like a store that helps customers choose the right products and provides excellent service to maintain them. The goal is to ensure customers leave satisfied and are eager to return.
Scope and Integration
CSM focuses on customer relationship management (CRM) systems, marketing tools, and ecommerce platforms to provide a holistic view of the customer journey, covering everything from purchase to post-sales service.
Now that we’ve discussed the basics of ServiceNow ITSM vs CSM, let’s dive deeper into the topic and discuss portal differences and processes.
CSM:
The CSM portal serves as the main customer-facing portal, similar to the entrance of a store or factory.
It is designed to be intuitive and easily accessible, helping customers find information, get support, and track the status of their issues.
ITSM:
The ITSM portal is exclusively for internal employees, offering private access for staff.
It is designed for employees to raise IT issues, request services, and access other internal resources.
In ITSM, the primary stakeholders are the IT teams, responsible for managing internal IT services and ensuring smooth operations.
On the other hand, CSM stakeholders include business teams and customer service representatives, who focus on managing customer interactions and ensuring satisfaction.
ITSM involves the delivery and management of information technology (IT) services that support business functions within an organization. The key processes within ITSM include:
1. Incident Management
Purpose: To restore normal operation of a service as quickly as possible and with the least impact on the business.
Process: Recognizing and logging an incident. Classifying and prioritizing the incident. Investigating and diagnosing the incident. Resolving and recovering from the incident. Closing the incident.
2. Problem Management
Purpose: To find the underlying cause of incidents and prevent the incidents from happening again. The problem will be classified as a known error or change if a solution to the incident has been found.
Process: Identifying and logging problems. Carrying out a root cause analysis. (If applicable) Identifying workarounds. Resolving the problem. Closing and documenting the problem.
3. Change Management
Purpose: To make sure that IT changes are deliberate and done with minimum disruption to the IT environment.
Process: Submitting the request for change (RFC). Assessing the impact and gaining approval. Planning and implementing the change. Reviewing the change after implementation.
4. Service Request Management
Purpose: To process service requests (e.g.: password reset, software access) quickly.
Process: Logging the service request. Gaining approval (if necessary). Fulfilling the user the request. Closing the request.
5. Asset and configuration management
Purpose: To maintain and manage IT assets and how they relate to each other in the Configuration Management Database (CMDB).
Process: Identifying and logging an asset in the CMDB. Managing an asset’s life cycle, acquisition, deployment, maintenance, and disposal. Ensuring the CMDB is correct and up to date.
6. Knowledge Management
Purpose: To have a central knowledge base which aids in getting incidents and problems resolved faster.
Process: Creating knowledge articles. Reviewing and publishing the knowledge articles. Using the knowledge articles and requesting feedback. Regularly updating knowledge articles.
7. IT Service Catalog Management
Purpose: To have a standardized catalog of IT services that could be offered to end users.
Process: Creating a service and categorizing the expectations. Managing a service request based on previously categorized expectations. Creating service fulfilment workflows for each service request.
8. SLA (Service Level Agreement) Management
Purpose: To have the ability to define an agreed service level that would be delivered.
Process: Defining agreed SLA agreements corresponding to incidents and service requests. Monitoring SLA compliances for each incident or service request. Escalation of incidents or service requests when an SLA breach has occurred.

CSM tackles all the customer-facing operations ensuring that every inquiry, complaint, and request is handled swiftly. In CSM, the main processes include:
1. Case Management
Purpose: To ensure all customer inquiries, complaints and problems are handled.
Process: Recording a case. These may be done by human efforts or by system- for example, via email, web, or phone). Ensuring everything is handled and resolved.
2. Omni-channel Support
Purpose: To allow the customer to optionally use any or multiple ways to get service. For example chat, email, phone, social media.
Process: Establishment of the communication channels. Agent interface for systems integrated channels. Providing service level across all the available channels for the queries received or handled and services provided through them.
3. Customer Request Management
Purpose: Address some client requests
Process: Request receipt. Forwarding it to concerned department. Example, IT teams or support. Fulfilling the request. Providing additional information and closing.
4. Field Service Management
Purpose: Control and plan provision of installation/repair/service by the company’s field technicians at the customer’s premises.
Process: Creating a case and organizing for field service activities. Assigning field technicians according to their proximity to the job, their skills and their availability. Actions and information updates of field management (on field technicians) through mobile systems. Closing of a case and any necessary follow-up.
5. Knowledge Management
Purpose: Enable customers to view FAQ, article, tutorial inclusive self-service portal.
Process: Writing knowledge articles for the customers to use. Maintaining the knowledge base on an ongoing basis. Recommending articles addressing customer’s questions. Asking for content enriching input from users.
Click here to download the overview as a PDF document.
You can schedule an expert call if you’re interested in learning more and are looking for a tailored approach for your organization.


Sign up to our monthly Flow@Work Exclusive newsletter to get free access to our expertise and lots of tips and tricks to make work flow on the Now® Platform.